eng
MTR — utility for checking the availability of a server or website, which shows the packet route to the service and losses at intermediate nodes.
MTR is a simple network diagnostic tool (service, server, website) from the command line or shell (WinMTR). It combines the functionality of traceroute and ping programs. Like traceroute, the mtr command displays information about the route, showing a list of nodes, routers through which the packet passes. However, mtr shows more information than traceroute: it determines the path to the remote server, shows response percentages and losses, as well as the response time of all network transitions in the route between your local system and remote servers. When should it be used? When there are suspicions of packet loss. With MTR, you can see if there is packet loss, check on which IP node packet loss occurs, after which you can find and determine the regional or backbone provider through which such a situation arose.
Checking on Windows OS
Download: WinMTR-v092.zip
In the program, for checking, specify the IP address of your server or domain name (only the site name without www or https).
For more detailed information, turn off "Resolve names" in the settings.
After sending at least 300 packets, save the result by clicking Export Text. Provide the support team with the verification results to the server for analysis. Or you can analyze it yourself according to the recommendations below.
Checking on Linux OS
On Debian family distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, etc.), you can install mtr with the command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt -y install mtrOn RHEL family distributions (CentOS, AlmaLinux, etc.), you can install mtr with the command:
sudo yum -y install mtrTo run the check on Linux, execute the command:
mtr --report -n -c 300 IPExecuting this command will take about 5-6 minutes.
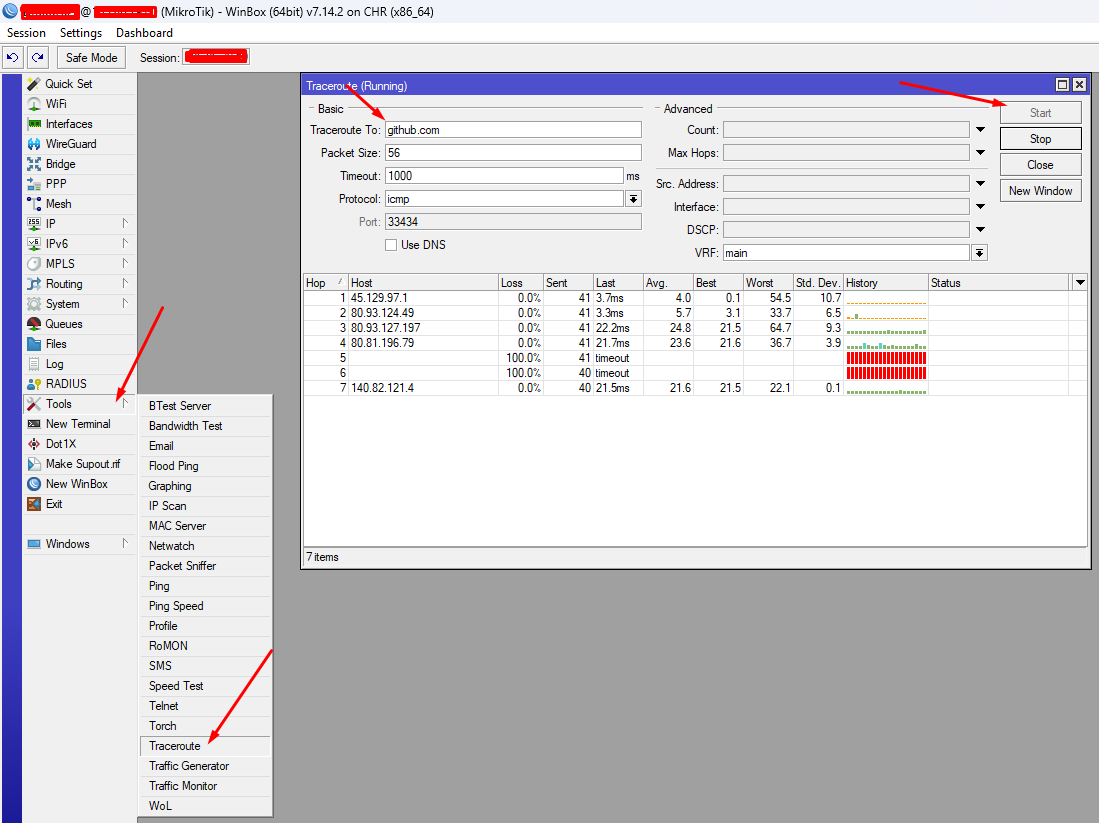
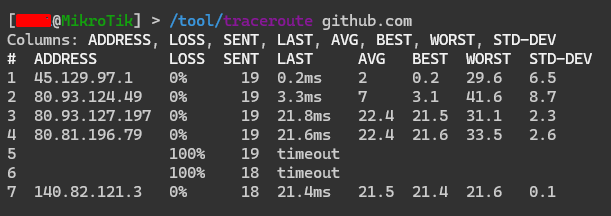
Checking on MikroTik RouterOS
On MikroTik devices, the MTR function is performed by the traceroute utility.
It can be found in: Tools -> Traceroute in Winbox, and /tool/traceroute in the console.
Where IP - IP node or domain name.
After execution, save a screenshot with the command execution results and attach it to the support ticket request for analysis by us. Or try to analyze it yourself.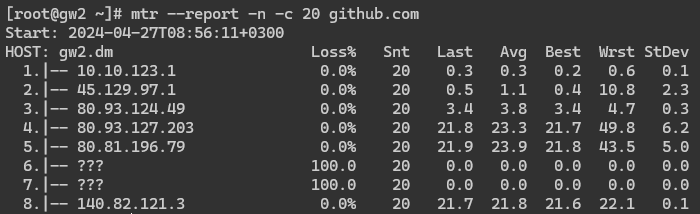
Explanation of WinMTR values and results
- Hostname - domain name or IP address of the node
- Nr – sequence number of the node in the route
- Loss % - percentage of lost request-response pairs from this site
- Sent - sent requests to this node
- Recv - received responses from it
- Best – the smallest (best) delay time
- Avrg – average delay time
- Worst – the largest (worst) delay time
- Last – time of the last received packet delay
The important parameter for us is Loss, the percentage of lost packets from the node. WinMTR uses the same ICMP protocol as the ping, tracert, pathping utilities. Cause for concern may be losses when Loss = 3-5% and more.
Analysis and results
Option 1. Packet loss at intermediate nodes
If losses are observed at intermediate nodes in the middle of the path, but there are no losses at the end nodes, it may be related to the settings of the nodes themselves. Typically, ICMP traffic has the lowest priority, so if a node is heavily loaded, MTR may show losses, but there are no problems with the main traffic. Or ICMP traffic may simply be blocked on the nodes, resulting in 100% losses on those nodes.
In these cases, "packet losses" do not mean actual losses, but only that the nodes are not responding to ICMP requests.
Option 2. Packet losses at end nodes
If packet losses with approximately the same percentage are observed at several end nodes, this may indicate problems with the carrier operators.
If packet losses are observed only at the last node (your server, router), this may indicate problems specifically with this device. In the case of a virtual server - high load/DDoS, or OS configuration issues. In the case of a dedicated server/router - unreliable network cable connections are added to the previous points.
In this case, checks need to be performed on the nodes themselves. You can perform checks yourself or contact our support for assistance.
For a comprehensive analysis, it is necessary to perform an MTR check in both directions: from your device to the server; and from the server to your router.
You can find out your external IP address for reverse checking, for example, using the service 2ip.ua. Or any other.
Reverse checking is necessary because packets go in both directions. First, a request goes from the initial node to the end node, and then a response goes from the end node to the initial node, and the problem could be anywhere.